Introduction to NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases have revolutionized the way organizations handle and manage data. Unlike traditional relational databases, which rely on structured schemas, NoSQL databases offer a flexible and scalable approach to storing and retrieving data. The term "NoSQL" stands for "not only SQL," indicating that these databases can handle diverse data types beyond the confines of a rigid tabular structure.
The main advantage of NoSQL databases is their ability to manage unstructured or semi-structured data efficiently. This makes them ideal for applications that deal with large volumes of complex and rapidly evolving data. With the rise of big data and the need for real-time analytics, NoSQL databases have become an essential tool for organizations seeking high performance, scalability, and flexibility.
Understanding Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has transformed the IT landscape, offering organizations an alternative to traditional on-premises infrastructure. By leveraging the power of the cloud, companies can access computing resources and services over the Internet, eliminating the need for costly hardware investments and maintenance.
Cloud computing provides numerous benefits when it comes to databases. The cloud offers virtually unlimited storage capacity, allowing organizations to scale their databases seamlessly as their data needs grow. Additionally, cloud providers offer built-in redundancy and high availability, ensuring data durability and minimizing the risk of data loss or downtime.
Cloud-based NoSQL databases combine the advantages of NoSQL technology with the scalability and resilience of the cloud. They enable organizations to handle massive amounts of data, deliver high-performance applications, and scale their infrastructure as needed, all without the burden of managing hardware or worrying about system failures.
Exploring NoSQL Database Models
NoSQL databases come in various models, each designed to cater to different data storage and retrieval requirements. Here are the four primary models of NoSQL databases:1. Key-value stores
Key-value stores are the simplest form of NoSQL databases. They store data as a collection of key-value pairs, where each value is associated with a unique key. Key-value stores excel in scenarios where fast and straightforward data retrieval is crucial. They are often used for caching, session management, and storing user preferences.
2. Document databases
Document databases store data in a flexible, schema-less manner. Data is organized as documents, typically in formats such as JSON or XML. This allows developers to store complex and nested data structures, making document databases well-suited for content management systems, e-commerce platforms, and applications that deal with semi-structured data.
3. Column-family stores
Column-family stores organize data into columns rather than rows. Each column can contain multiple versions of a value, making it efficient for scenarios that require write-intensive operations. Column-family stores are commonly used in time-series data analysis, content management systems, and social media analytics.
4. Graph databases
Graph databases are designed to handle highly interconnected data. They store data as nodes, edges, and properties, enabling efficient representation and traversal of complex relationships. Graph databases excel in use cases such as social networks, recommendation engines, and fraud detection systems, where uncovering patterns and relationships between entities is crucial.
Benefits of Cloud NoSQL Databases
Utilizing NoSQL databases in the cloud offers several advantages for organizations:
1. Scalability and flexibility
Cloud NoSQL databases provide horizontal scalability, meaning they can handle increased workloads by distributing data across multiple servers. This enables organizations to accommodate growing data volumes and handle high traffic loads without sacrificing performance. Additionally, NoSQL databases offer flexible data models, allowing for agile development and the ability to adapt to evolving business requirements.
2. High availability and fault tolerance
Cloud NoSQL databases leverage the infrastructure of cloud providers, which are designed to ensure high availability and fault tolerance. Data is replicated across multiple servers and data centres, minimizing the risk of data loss and providing resilience against hardware failures. In the event of a server or data centre outage, the database seamlessly switches to a replica, ensuring continuous access to data and minimal disruption to the application.
3. Cost-effectiveness and pay-as-you-go model
Cloud-based NoSQL databases eliminate the need for organizations to invest in and maintain their physical servers. This reduces upfront costs and ongoing expenses related to hardware procurement, infrastructure management, and software licenses. Cloud providers offer a pay-as-you-go pricing model, where organizations only pay for the resources they consume, making it cost-effective and scalable as per the business needs.
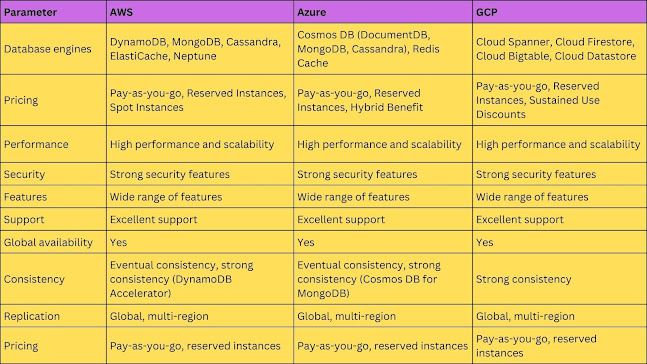
Popular Cloud NoSQL Databases
Several cloud providers offer robust NoSQL database services that leverage the power of the cloud:
1. Amazon DynamoDB
Amazon DynamoDB, provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS), is a fully managed NoSQL database service. DynamoDB offers seamless scalability, low latency, and automatic data replication across multiple Availability Zones. It provides a reliable and highly available database solution, making it well-suited for various use cases, including gaming, ad tech, and Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
2. Google Cloud Firestore
Google Cloud Firestore is a serverless NoSQL database service offered by Google Cloud. It provides real-time synchronization, offline support, and automatic scaling. Firestore is designed for mobile and web applications that require real-time collaboration, offline capabilities, and seamless data synchronization across devices. It offers a flexible data model and easy integration with other Google Cloud services.
3. Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB
Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB is a globally distributed, multi-model database service. It supports various NoSQL models, including key-value, document, column-family, and graph databases. Cosmos DB offers low latency, global scalability, and automatic indexing, making it suitable for global applications with low-latency requirements. It provides developers with the flexibility to choose the most appropriate data model for their application and offers comprehensive SLAs for performance, availability, and data consistency.
4. MongoDB Atlas
MongoDB Atlas is a cloud-based, fully managed NoSQL database service provided by MongoDB. It offers a scalable, secure, and highly available platform for deploying MongoDB databases. MongoDB Atlas simplifies database management tasks, allowing developers to focus on building applications rather than worrying about infrastructure. It provides comprehensive monitoring, automated backups, and advanced security features to protect data.
Considerations for Choosing a Cloud NoSQL Database
When selecting a cloud NoSQL database, organizations should consider the following factors: 1. Data model requirements
Different NoSQL models are optimized for specific data structures and use cases. It is essential to evaluate the requirements of the application and choose a database model that aligns with the data access patterns and query needs.
2. Scalability and performance needs
Scalability is a critical aspect of cloud NoSQL databases. Organizations should assess their scalability requirements and ensure that the chosen database can handle the expected workload without compromising performance. It is crucial to consider factors such as read and write throughput, data partitioning, and the ability to handle peak traffic.
3. Integration with existing systems
Organizations often have existing systems and applications that need to interact with the chosen NoSQL database. Compatibility and integration capabilities should be evaluated to ensure a seamless integration process and minimize disruption to the existing infrastructure.
4. Cost considerations
While cloud NoSQL databases offer cost savings compared to on-premises solutions, organizations should evaluate the pricing models, including storage costs, data transfer fees, and pricing tiers based on performance requirements. It is essential to choose a database that aligns with the budget and provides cost transparency.
Best Practices for Implementing Cloud NoSQL Databases
To maximize the benefits of cloud NoSQL databases in the cloud, organizations should follow the best practices for implementation:
1. Data modelling and schema design
Careful consideration should be given to data modelling and schema design. This involves understanding the application's data access patterns and structuring the data in a way that optimizes query performance. Denormalization and embedding related data can improve query efficiency in document databases, while thoughtful column design enhances performance in column-family stores.
2. Indexing and querying techniques
Efficient indexing and querying are crucial for retrieving data quickly. NoSQL databases provide various indexing options to optimize query performance. Organizations should analyze query patterns and create appropriate indexes to ensure fast and accurate data retrieval. Query optimization techniques, such as avoiding full table scans and utilizing selective projections, should be employed to minimize query execution time.
3. Security and access control
Data security is a top priority for organizations. When implementing a cloud NoSQL database, robust security measures should be put in place. This includes encrypting data at rest and in transit, implementing access controls and authentication mechanisms, and regularly monitoring and auditing access logs. Compliance with industry standards and regulations should also be ensured.
4. Monitoring and optimization
Monitoring the performance and health of the cloud NoSQL database is essential to identify bottlenecks, detect anomalies, and optimize resource utilization. Utilizing monitoring tools provided by the cloud provider or implementing third-party monitoring solutions allows organizations to proactively identify and address performance issues. Optimization techniques, such as fine-tuning resource allocation and query optimization, should be applied regularly to maintain optimal database performance.
Differences between NoSQL databases and SQL databases:
1. Data Model:
- NoSQL: NoSQL databases use a flexible and schema-less data model that allows for the storage of unstructured or semi-structured data.
- SQL: SQL databases use a structured data model based on tables, rows, and columns that defines the structure and relationships of the data.
2. Scalability:
- NoSQL: NoSQL databases are designed for horizontal scalability, allowing them to handle large volumes of data and high traffic loads by adding more servers to the database cluster.
- SQL: SQL databases traditionally rely on vertical scalability, requiring hardware upgrades to handle increased workloads.
3. Query Language:
- NoSQL: NoSQL databases use various query languages or APIs specific to the database technology being used.
- SQL: SQL databases use standardized SQL (Structured Query Language) for querying and manipulating data.
4. Data Relationships:
- NoSQL: NoSQL databases do not enforce strict relationships between data entities. They prioritize flexibility and scalability, allowing data relationships to be represented using embedded documents, arrays, or graph-based approaches.
- SQL: SQL databases rely on well-defined relationships between tables using primary and foreign keys. They enforce data integrity through relationships, ensuring consistency and referential integrity across tables.
5. ACID Transactions:
- NoSQL: NoSQL databases typically prioritize availability and scalability over strong transactional consistency. They often provide eventual consistency, where updates may take time to propagate across all replicas in a distributed system.
- SQL: SQL databases prioritize strong ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) transactions, ensuring that data remains consistent and durable even in the presence of failures. ACID compliance is a fundamental feature of SQL databases.
Challenges and Limitations of Cloud NoSQL Databases
While cloud NoSQL databases offer numerous benefits, there are also challenges and limitations to consider:
1. Lack of standardized query language
Unlike SQL databases, which use a standardized query language (SQL), NoSQL databases often have their own query languages or APIs. This can create a learning curve for developers and require specific knowledge of the database's query interface.
2. Data consistency and transactional support
Maintaining strong consistency across distributed NoSQL databases can be challenging. Some NoSQL databases prioritize availability and partition tolerance over strong consistency, offering eventual consistency instead. Organizations should assess their data consistency requirements and select a database that aligns with their needs. Transactional support can also vary across different NoSQL databases, requiring careful consideration for applications that require ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) properties.
3. Vendor lock-in and migration challenges
Migrating from one cloud NoSQL database to another or from the cloud to an on-premises infrastructure can be complex and time-consuming. Organizations should be aware of the potential vendor lock-in and evaluate the ease of migration and data portability options when selecting a cloud NoSQL database.
Conclusion
NoSQL databases have transformed the way organizations handle and process data, providing scalable, flexible, and high-performance solutions. Combining NoSQL databases with the power of the cloud further enhances these advantages, allowing organizations to leverage the scalability, availability, and cost-effectiveness of cloud computing.
Cloud NoSQL databases offer various models, each tailored to specific use cases, such as key-value stores, document databases, column-family stores, and graph databases. Popular cloud providers, including Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure, offer robust NoSQL database services that cater to diverse application requirements.
When implementing a cloud NoSQL database, organizations should consider factors such as data model requirements, scalability needs, integration capabilities, and cost considerations. Following best practices for data modelling, indexing, security, and optimization ensures optimal performance and data integrity.
While challenges such as a lack of standardized query language and data consistency issues exist, the benefits of cloud NoSQL databases outweigh these limitations. With the continuous advancements in NoSQL technology and cloud computing, the future holds even more promising opportunities for organizations to leverage the power of NoSQL databases in the cloud.
FAQs
What is the difference between NoSQL and SQL databases?
NoSQL databases differ from SQL databases in their data model and storage approach. NoSQL databases provide flexibility to handle unstructured and semi-structured data, while SQL databases follow a structured, tabular format. NoSQL databases excel in scalability and performance for large-scale data, while SQL databases provide transactional consistency and support for complex queries.
Can I use a cloud NoSQL database with my existing SQL database?
Yes, using a cloud NoSQL database alongside an existing SQL database is possible. Many applications have a hybrid architecture where SQL databases are used for structured data and transactions, while NoSQL databases handle unstructured or high-volume data.
How do I ensure data security in a cloud NoSQL database?
Data security in a cloud NoSQL database can be ensured by implementing encryption at rest and in transit, using strong access controls and authentication mechanisms, and regularly monitoring access logs for any suspicious activity. Following security best practices and compliance standards helps protect sensitive data.
What are the typical use cases for cloud NoSQL databases?
Cloud NoSQL databases are suitable for a wide range of use cases, including real-time analytics, content management systems, e-commerce platforms, social networks, recommendation engines, and Internet of Things (IoT) applications. Their scalability, flexibility, and ability to handle diverse data types make them valuable for modern applications dealing with large volumes of data.
Are there any limitations on the size of data I can store in a cloud NoSQL database?
Cloud NoSQL databases offer virtually unlimited storage capacity, allowing organizations to store large volumes of data. However, it's important to consider the pricing and performance implications of storing and accessing vast datasets. Organizations should assess their specific requirements and consult with the cloud provider to determine the optimal storage configuration.
Can NoSQL databases handle structured data?
NoSQL databases are primarily designed to handle unstructured and semi-structured data. While they can accommodate structured data to some extent, their main strength lies in storing and retrieving unstructured data efficiently. If your application relies heavily on structured data and complex relationships, a SQL database may be a more suitable choice.
Are SQL databases suitable for handling unstructured data?
SQL databases are not typically designed for handling unstructured data. They excel at managing structured data with predefined schemas and enforcing data integrity through relationships. If your application deals with large amounts of unstructured data, such as text documents or multimedia content, NoSQL databases, especially document-oriented ones, maybe a better fit.
Which type of database is more scalable?
Both NoSQL and SQL databases can be scaled to handle large amounts of data and high traffic loads. However, the scalability approach differs between the two. NoSQL databases are designed for horizontal scalability, allowing you to distribute the data across multiple servers or clusters easily. SQL databases can be vertically scaled by increasing the resources of a single server, but scaling horizontally involves additional complexities.
Do NoSQL databases support transactions?
NoSQL databases vary in terms of their support for transactions. While some NoSQL databases provide ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) properties and support transactions, others may prioritize scalability and performance over strict transactional guarantees. It's important to carefully evaluate the specific NoSQL database you're considering to determine its transactional capabilities.
Can I use both NoSQL and SQL databases together in an application?
Yes, it's possible to use both NoSQL and SQL databases together in an application. This approach, known as polyglot persistence, allows you to leverage the strengths of each database type for different parts of your application. For example, you might use a SQL database for structured data with complex relationships and a NoSQL database for storing unstructured or rapidly changing data. However, it's essential to consider the additional complexity and potential synchronization challenges that may arise when working with multiple databases.

.jpg)




.png)







